Test de dépistage de la schizophrénie en ligne : Symptômes, causes et guide de soutien
October 30, 2025 | By Julian Shepherd
Introduction : Démystifier la schizophrénie : Un aperçu complet
La schizophrénie est un terme souvent entouré de nombreux malentendus. C'est une maladie mentale complexe qui peut entraîner un sentiment d'isolement pour ceux qui en souffrent et de confusion pour leurs proches. Si vous cherchez des réponses concernant vos propres expériences ou celles d'une personne qui vous est chère, vous n'êtes pas seul. La compréhension est le premier pas vers la clarté. Beaucoup de gens se demandent : "Ai-je la schizophrénie ?" lorsqu'ils sont confrontés à des changements troublants dans leurs pensées ou leurs sentiments. Ce guide fournit des informations claires et bienveillantes et montre comment un test préliminaire de schizophrénie peut être un point de départ sûr. Pour une première clarté, un outil de dépistage confidentiel offre de précieuses informations privées.

Comprendre la schizophrénie : Au-delà des idées reçues
La schizophrénie est un trouble cérébral grave qui affecte la façon dont une personne pense, ressent et se comporte. Ce n'est pas une "double personnalité" – un mythe courant – mais une perte de contact avec la réalité. Comprendre cette distinction est crucial pour aborder le sujet avec empathie. La maladie apparaît souvent à la fin de l'adolescence ou au début de l'âge adulte, une période critique de la vie, ce qui rend la sensibilisation précoce incroyablement importante.
Définir la schizophrénie : Un trouble cérébral complexe
La schizophrénie est caractérisée par des épisodes de psychose, où les pensées et les perceptions d'une personne sont altérées. Elle peut affecter sa capacité à gérer ses émotions, à interagir avec les autres et à fonctionner dans la vie quotidienne. C'est une condition médicale nécessitant des soins et une prise en charge, et non un défaut de caractère. L'expérience varie grandement d'une personne à l'autre, avec des symptômes et des niveaux de gravité différents.
Signes précoces et comment la schizophrénie débute
Comment se manifeste la schizophrénie au début ? Le début est souvent progressif, avec des changements subtils qui peuvent être confondus avec un comportement adolescent typique ou le stress. Cette phase précoce est appelée la période "prodromique". Les signes avant-coureurs peuvent inclure le retrait social, une baisse des performances scolaires ou professionnelles, des difficultés de concentration et un manque général de motivation. Reconnaître ces premiers changements peut être la clé pour obtenir de l'aide plus tôt. Une auto-évaluation gratuite peut aider à organiser ces expériences précoces confuses.
Reconnaître les symptômes et les signes de la schizophrénie
Les symptômes de la schizophrénie sont généralement classés en trois groupes principaux : positifs, négatifs et cognitifs. Comprendre ces catégories aide à brosser un tableau plus complet de ce à quoi la maladie peut ressembler. Bien que tout le monde ne présente pas tous les symptômes, reconnaître ces schémas est une étape essentielle pour rechercher une évaluation professionnelle.
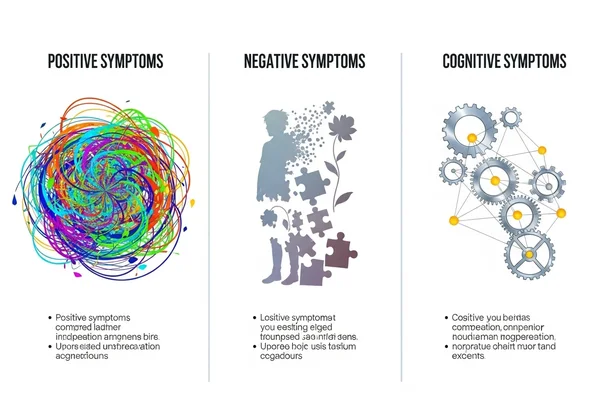
Symptômes positifs : Hallucinations, délires et pensée désorganisée
Les symptômes positifs sont des comportements psychotiques généralement absents chez les personnes en bonne santé, représentant un excès ou une distorsion des fonctions normales. Ce sont souvent les symptômes les plus alarmants et ils incluent :
- Hallucinations : Entendre, voir ou ressentir des choses qui ne sont pas là. Les hallucinations auditives, comme entendre des voix, sont les plus courantes.
- Délires : Croyances fausses et fermement ancrées qui ne sont pas basées sur la réalité, comme croire qu'on est persécuté ou qu'on a des pouvoirs spéciaux.
- Pensée désorganisée : Difficulté à organiser les pensées, ce qui conduit à un discours incohérent difficile à suivre pour les autres.
- Comportement moteur désorganisé : Cela peut aller de la puérilité à une agitation imprévisible.
Symptômes négatifs : Impact sur la motivation et l'émotion
Les symptômes négatifs désignent une réduction ou une absence de comportements normaux. Ils sont plus difficiles à reconnaître comme faisant partie d'un trouble et sont souvent confondus avec la dépression ou la paresse. Ils incluent l'« émoussement affectif » (réduction de l'expression des émotions), la perte de plaisir dans la vie quotidienne, une capacité diminuée à initier et à maintenir des activités planifiées, et une réduction de la parole. Ces symptômes peuvent avoir un impact significatif sur le fonctionnement social.
Symptômes cognitifs : Difficultés de mémoire, d'attention et de traitement
Les symptômes cognitifs peuvent être subtils ou graves, interférant avec le « fonctionnement exécutif » – la capacité à traiter l'information et à prendre des décisions. Ils incluent une faible capacité à se concentrer ou à prêter attention, des difficultés avec la mémoire de travail (la capacité à utiliser l'information immédiatement après l'avoir apprise) et des difficultés à traiter l'information. Si vous vous interrogez sur ces signes, un test de schizophrénie en ligne peut constituer un point de départ utile pour une discussion avec un professionnel.
Explorer les causes de la schizophrénie
Il n'existe pas de cause unique à la schizophrénie. Au lieu de cela, les chercheurs pensent qu'une combinaison de facteurs génétiques, biologiques et environnementaux contribue à son développement. Comprendre ces causes potentielles peut aider à démystifier la maladie et à réduire l'auto-culpabilisation.
Facteurs génétiques : La schizophrénie est-elle héréditaire ?
La génétique joue un rôle significatif. Bien que la maladie se retrouve dans les familles, avoir un membre de la famille atteint de schizophrénie ne signifie pas que vous la développerez nécessairement. Cependant, cela augmente le risque. Le risque est complexe ; plusieurs gènes sont considérés comme impliqués, et votre constitution génétique globale, et non un seul gène d'un parent, contribue au risque.
Chimie et structure du cerveau : La base biologique
Les neurotransmetteurs – des substances chimiques qui transmettent des signaux entre les cellules du cerveau – sont censés jouer un rôle clé. En particulier, un déséquilibre dans les systèmes de dopamine et de glutamate est associé à la schizophrénie. De plus, des différences subtiles dans la structure du cerveau, telles que des ventricules légèrement plus grands ou une réduction de la matière grise dans certaines zones, sont parfois observées chez les personnes atteintes de cette condition.
Déclencheurs environnementaux et facteurs de risque
Bien qu'une personne puisse être génétiquement prédisposée à la schizophrénie, des facteurs environnementaux peuvent agir comme des déclencheurs. Ceux-ci peuvent inclure l'exposition à des virus ou à la malnutrition avant la naissance, des problèmes pendant l'accouchement et des facteurs psychosociaux comme le fait de subir un traumatisme ou de vivre dans un environnement très stressant. La consommation de drogues psychoactives pendant l'adolescence et le jeune âge adulte peut également augmenter le risque.
Diagnostiquer la schizophrénie : L'approche professionnelle
Un diagnostic définitif de schizophrénie ne peut être posé que par un professionnel de la santé qualifié, tel qu'un psychiatre. Il n'existe pas de test de laboratoire unique pour la schizophrénie. Au lieu de cela, le diagnostic implique une évaluation complète pour écarter d'autres conditions médicales ou l'usage de substances qui pourraient causer les symptômes.
Quels tests confirment la schizophrénie ? Évaluation clinique et critères
Une évaluation professionnelle comprend une évaluation psychiatrique des symptômes, un examen des antécédents médicaux personnels et familiaux, et parfois un examen physique et des analyses sanguines pour éliminer d'autres possibilités. Le clinicien utilisera les critères diagnostiques décrits dans le Manuel diagnostique et statistique des troubles mentaux (DSM-5) pour déterminer si les symptômes spécifiques et leur durée correspondent au seuil diagnostique.
Le rôle des auto-évaluations : Premières idées et prochaines étapes
C'est là que les outils en ligne peuvent être incroyablement utiles. Bien qu'ils ne puissent pas vous diagnostiquer, un test de schizophrénie gratuit et confidentiel sert de précieux dépistage préliminaire. Il peut vous aider à organiser vos pensées et vos expériences, vous donnant une image plus claire de la question de savoir si vos préoccupations nécessitent une consultation professionnelle. Considérez-le comme une première étape privée pour obtenir un aperçu. Passer un test de schizophrénie en ligne peut vous fournir un résumé à partager avec un médecin, rendant cette première conversation moins intimidante.
Traitement et soutien pour vivre avec la schizophrénie
Bien qu'il n'existe pas de remède à la schizophrénie, c'est une condition hautement traitable. Avec la bonne combinaison de traitements et de soutien, de nombreuses personnes peuvent gérer leurs symptômes, réduire les rechutes et mener une vie épanouissante et autonome. La clé est un traitement précoce et constant.

Approches de traitement modernes : Médication et thérapie
Les médicaments antipsychotiques sont la pierre angulaire du traitement, aidant à gérer les symptômes les plus graves comme les hallucinations et les délires. Les traitements psychosociaux sont tout aussi importants. Ceux-ci incluent des thérapies comme la thérapie cognitivo-comportementale (TCC), qui aide à modifier les schémas de pensée et de comportement, ainsi que l'éducation familiale et les groupes de soutien.
Peut-on se rétablir complètement de la schizophrénie ? Se concentrer sur la gestion et la qualité de vie
Le concept de "rétablissement" a évolué. Pour beaucoup, le rétablissement signifie apprendre à gérer la maladie pour atteindre des objectifs personnels et maintenir une qualité de vie élevée, tandis que certains peuvent connaître une disparition complète des symptômes. Avec un traitement efficace, de nombreuses personnes peuvent travailler, avoir des relations et être des membres actifs de leur communauté. L'espoir est une partie essentielle du parcours.
Construire un système de soutien : Ressources pour les individus et les familles
Un solide système de soutien est essentiel. Cela inclut la famille, les amis et les groupes de soutien par les pairs. Éduquer les proches sur la maladie les aide à comprendre ce que vous traversez et à fournir un soutien efficace. Les services communautaires de santé mentale peuvent également offrir une gestion de cas pour aider avec le logement, l'emploi et d'autres besoins pratiques.
Agir pour votre santé mentale
Comprendre la schizophrénie – ses symptômes, ses causes et ses traitements – est une étape puissante pour démystifier la maladie et réduire la stigmatisation. Cela transforme la peur de l'inconnu en une recherche proactive de connaissances et de soutien. Si vous ou quelqu'un que vous connaissez présentez des symptômes confus, rappelez-vous qu'une prise de conscience et une action précoces sont cruciales. Vous n'avez pas à naviguer seul dans cette incertitude.
Effectuer un dépistage préliminaire confidentiel peut être un moyen simple et privé d'évaluer vos expériences. Il fournit des informations immédiates qui peuvent vous donner les moyens de passer à l'étape suivante. Nous vous encourageons à essayer notre outil gratuit dès aujourd'hui. C'est un premier pas responsable sur votre chemin vers le bien-être mental.
Questions fréquemment posées sur la schizophrénie
Ai-je la schizophrénie ? Comment puis-je le savoir ?
La seule façon d'en être certain est d'être évalué par un professionnel de la santé mentale. Cependant, si vous êtes inquiet, une bonne première étape consiste à effectuer un dépistage en ligne confidentiel, comme le test d'évaluation de la schizophrénie disponible sur notre site. Il peut vous aider à comprendre si vos symptômes correspondent aux signes précoces et vous fournir un point de départ pour une conversation avec un médecin.
Quels sont les premiers signes de la schizophrénie ?
Les premiers signes incluent souvent le retrait social, une baisse de fonctionnement à l'école ou au travail, des changements dans l'hygiène personnelle, des difficultés de concentration et l'expression d'idées inhabituelles ou suspectes. Ces changements sont souvent progressifs et peuvent être difficiles à repérer au début.
Peut-on se rétablir complètement de la schizophrénie ?
Bien que la schizophrénie soit généralement une maladie chronique, le « rétablissement » est absolument possible. Pour beaucoup, le rétablissement signifie gérer avec succès les symptômes et vivre une vie pleine et productive. Avec un traitement constant, incluant des médicaments et une thérapie, les perspectives sont bien plus encourageantes qu'elles ne l'étaient par le passé.
À quoi ressemble la « schizophrénie légère » ?
Le terme « forme légère de schizophrénie » n'est pas un diagnostic officiel, mais il peut désigner une personne qui présente des symptômes moins nombreux, moins intenses ou moins fréquents. Il pourrait également décrire une personne en phase « prodromique » précoce ou un individu dont les symptômes sont bien gérés par le traitement. Leurs défis pourraient être moins perturbateurs pour la vie quotidienne mais nécessitent toujours un soutien. Un dépistage préliminaire peut aider à identifier même des schémas subtils.