How Schizophrenia Develops: Early Signs, Progression & Testing
December 5, 2025 | By Julian Shepherd
The early stages of potential mental health conditions can be confusing and frightening. Are you noticing subtle changes in your thoughts, feelings, or behaviors? Or have you seen these changes in someone you care about? Understanding how schizophrenia develops is the first step toward finding clarity and support. This condition rarely appears overnight. Instead, it typically progresses from subtle initial signs to more noticeable symptoms.
Understanding how schizophrenia develops can help demystify this complex condition. We'll explore the earliest warning signs in the prodromal phase, the symptoms of the active phase, and the importance of professional diagnosis. Gaining knowledge empowers you to take meaningful action. For a private, preliminary look at your experiences, a free self-assessment can provide valuable initial insights.
Identifying the Earliest Indicators: The Prodromal Phase
Before the more commonly known symptoms of schizophrenia appear, there is often a period of gradual change known as the prodromal phase. During this time, a person’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors may begin to shift, but the changes can be subtle and easily mistaken for other issues, like stress or typical teenage moodiness. Recognizing these early indicators is crucial for seeking help sooner.
Subtle Changes and Initial Warning Signs
The warning signs during the prodromal phase are often non-specific, meaning they could be caused by many different things. However, a pattern of these changes can be a signal to pay closer attention. Some of the most common early indicators include:
- Social Withdrawal: Losing interest in spending time with friends and family, preferring to be alone.
- Decline in Functioning: A noticeable drop in performance at school or work, or difficulty managing daily responsibilities.
- Changes in Personal Hygiene: Neglecting grooming or personal care.
- Emotional Blunting: Appearing unusually apathetic, with a reduced range of emotional expression.
- Anxiety and Suspiciousness: Feeling increasingly anxious, paranoid, or suspicious of others without a clear reason.
- Unusual Thoughts or Beliefs: Developing peculiar ideas or preoccupations that seem strange to others.
- Perceptual Disturbances: Fleeting or mild experiences, like thinking you hear someone call your name or seeing shadows in the corner of your eye.
These signs do not mean someone definitely has schizophrenia, but they are worth noting, especially if they persist or worsen.
Recognizing the Characteristics of the Prodromal Period
The prodromal period is the "ramp-up" phase. It can last anywhere from a few months to a few years. During this time, the individual may feel that something is "off" but be unable to articulate what is wrong. They might struggle with concentration, motivation, and sleep.
For family and friends, this can be a confusing time. A loved one might seem like a different person—more withdrawn, irritable, or lost in their own thoughts. It’s important to approach the situation with compassion and patience. Understanding that these changes could be part of an underlying health issue is key. A confidential online schizophrenia test can be a helpful tool for organizing these observations into a clearer picture.
Understanding the Active Phase and Professional Diagnosis
When symptoms become more severe, frequent, and disruptive to daily life, the condition may be entering the active phase. This is when a professional diagnosis is typically made. It's vital to remember that only a qualified healthcare professional, such as a psychiatrist, can diagnose schizophrenia.
Common Symptoms During an Active Schizophrenic Episode
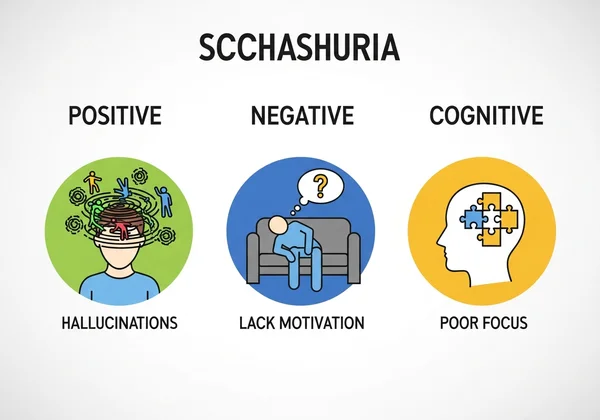
The symptoms of active schizophrenia are generally grouped into three categories: positive, negative, and cognitive.
-
Positive Symptoms: These are experiences that are "added" to a person's reality. They include:
- Hallucinations: Seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not there. Auditory hallucinations (hearing voices) are most common.
- Delusions: Holding strong, false beliefs that are not based in reality, such as believing one is being followed or has special powers.
- Disorganized Thinking/Speech: Difficulty organizing thoughts, leading to speech that is jumbled and hard to follow.
-
Negative Symptoms: These refer to a "loss" or reduction in normal abilities and emotions. They include:
- Alogia: A reduction in the amount of speech.
- Avolition: A significant lack of motivation to engage in purposeful activities.
- Anhedonia: The inability to experience pleasure.
- Flat Affect: A diminished emotional expression in the face or voice.
-
Cognitive Symptoms: These involve problems with thought processes, such as:
-
Poor Executive Functioning: Difficulty understanding information and using it to make decisions.
-
Trouble with Focus: Inability to pay attention or concentrate.
-
Problems with Working Memory: Difficulty using information immediately after learning it.
-
The Process of Clinical Assessment and Official Diagnosis
Confirming a schizophrenia diagnosis is a comprehensive process. A doctor will conduct a full psychiatric evaluation, which includes discussing symptoms, personal history, and family history. They will also work to rule out other medical or mental health conditions that could cause similar symptoms, such as bipolar disorder, severe depression, or substance use.
There is no single blood test or brain scan for schizophrenia. The diagnosis is based on observing signs and symptoms over time and matching them to the criteria outlined in diagnostic manuals like the DSM-5. While an online screening can't provide a diagnosis, taking a schizophrenia test free can help you prepare for a conversation with a doctor by identifying key experiences to discuss.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Ongoing Support
One crucial insight from understanding schizophrenia is that early intervention makes a significant difference. Identifying warning signs during the prodromal phase and seeking help can significantly improve long-term outcomes and quality of life.
Why Early Recognition Can Make a Significant Difference
Acting on the early signs of schizophrenia is one of the most powerful things you can do for yourself or a loved one. Early treatment can help:
- Slow or stop the progression of the illness.
- Reduce the severity of symptoms in the long run.
- Minimize disruption to education, career, and relationships.
- Improve the overall chances of recovery and successful management.
- Lower the risk of secondary problems like depression or substance abuse.
Taking a proactive approach starts with acknowledging that something might be wrong. Using a tool to gain preliminary insights is a brave and responsible first step in this journey.
Building a Support Network and Effective Management Strategies
Managing schizophrenia is a lifelong journey, and a strong support system is essential. For the individual, this means having trusted family, friends, and healthcare professionals to rely on. For supporters, it means learning about the condition, offering non-judgmental support, and encouraging consistent treatment.
Effective management strategies often include a combination of medication, psychotherapy (like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy), and social support programs. Learning to manage stress, maintain a healthy routine, and identify symptom triggers are all key components of living well with the condition.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge and Action
Understanding the progression of schizophrenia—from the subtle prodromal phase to the active phase—removes much of the fear associated with the unknown. It shows that there are signs to watch for and opportunities to act early. Knowledge gives you the power to observe changes in yourself or others with clarity instead of panic.
If you are concerned, you don't have to navigate these feelings alone. The most important step is seeking information and support. Your journey to understanding can begin right now, in a safe and confidential way.

Take the next step toward clarity. Visit SchizophreniaTest.net to take a free, confidential self-assessment based on established early screening methods. It can help you organize your thoughts and provide valuable insights as you consider speaking with a healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia Progression
How Does Schizophrenia Typically Start Off?
Schizophrenia usually starts off gradually during what is known as the prodromal phase. This period is characterized by subtle changes in behavior, thoughts, and mood, such as increased social withdrawal, a decline in school or work performance, and mild anxiety or suspiciousness. These early signs can often be mistaken for other issues before more distinct symptoms appear.
What Are the Earliest Signs of Schizophrenia in Young Adults?
In teenagers and young adults, the earliest signs often involve changes in social and academic life. You might notice them losing friends, their grades dropping, or them becoming more irritable and isolated. They may also develop unusual interests or express strange ideas. Because this can overlap with typical adolescent behavior, it's the pattern and persistence of these signs that matter. An early signs of schizophrenia test can help clarify if these concerns warrant professional attention.
Can Schizophrenia Symptoms Appear Mild or Gradually Worsen?
Yes, absolutely. The onset of schizophrenia is rarely sudden. Symptoms often start mild and worsen over months or even years. What begins as a vague feeling of being "different" or mild perceptual disturbances can slowly progress into more pronounced hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking during the active phase of the illness.
What Kind of Tests Are Used to Confirm a Schizophrenia Diagnosis?
There is no single lab test, blood test, or brain scan that can confirm a schizophrenia diagnosis. A qualified healthcare professional makes a diagnosis through a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation. This process includes in-depth interviews, behavior observation, and ruling out other medical or psychiatric conditions. While online screening tools like a free schizophrenia test aren't diagnostic, they provide valuable preliminary insights. These tools help you identify and organize symptoms to discuss with your doctor.
Is Full Recovery from Schizophrenia Possible with Early Intervention?
While schizophrenia is a chronic condition, significant recovery is possible, especially with early intervention. "Recovery" means learning to manage symptoms effectively and leading a full, productive, and meaningful life. With the right combination of medication, therapy, and a strong support system, many people with schizophrenia can finish their education, maintain careers, and enjoy fulfilling relationships. Early treatment greatly improves these outcomes.